- Mandatory / Hard Logic
- Inherent in the nature of work done. - External
- Based on the needs of a party outside of the project. - Discretionary
- Dependencies defined by Project Management Team at their discretion.
- There is no choice between Mandatory and External Dependencies.
- This is the preferred method of arranging activities based on conditions, guidelines or best practices.
This site contains information for your preparation of PMI's PMP (Project Management Professional) certification exam. I have also Included topics on how to pass the exam and some mock exams.
Saturday, December 29, 2007
Activity Dependencies
Sunday, December 23, 2007
Facelift for PMP® and CAPM® Score Reports
Please note that recent change to PMP score reports. To me, this seems to be a good idea where more details on your scores will be provided if you fail the test. More information, you may want to refer to PMI website.
With the launch of the PgMPSM credential on 1 October 2007, PMI instituted a new look for its score reports. This new look will also appear on the PMP and CAPM score reports by the end of the year.
Q: What information is provided on the new score report?
A: Just as before, there are two levels of information provided. One is the overall examination results, which will tell you whether you passed or failed. The other is a diagnostic representation of your proficiency level per domain for PMP and PgMP and by chapter for CAPM. Each domain or chapter is accompanied by one of three possible proficiency levels—Proficient, Moderately Proficient, and Below Proficient.
Q: Why did PMI change the score report?
A: PMI improved how the diagnostic results are presented in the score reports. Instead of percentages by domain/chapter, PMI is instituting global best practices in examination administration by using proficiency levels.
Q: How can the proficiency levels guide my professional development?
A: The proficiency levels serve as an aid in measuring your knowledge in specific areas of study and practice. For example, if your result is Below Proficient in one of the domains/chapters, you then know what you need to study to improve.
Q: What else has changed in PMI’s examination practices?
A: Nothing. The credential examinations remain the same.
Q: Does the change in the score report indicate a different score or standard to pass the examination?
A: No. Results are based on the same scoring standards as before. This means that people who receive the new score report are evaluated the same way as those who received the old score report.
Q: Do I have to be proficient in every domain in order to pass the examination?
A: No. There are not a minimum or maximum number of domains in which you need to demonstrate proficiency in order to pass the exam. Your pass/fail rate is determined based on your overall performance, not on how many questions you answered right or wrong in a particular domain.
Friday, December 21, 2007
What is Activity Sequencing and Activity Dependency in PMP
- a planning method for the purpose of creating the project schedule.
- identifying and documenting interactivity dependencies among project activities.
Activity Dependency is:
- a logical relationship that exists between 2 project activities.
- the sequence among project activities.
Saturday, December 15, 2007
What is Activity?
- must be performed to produce the project's deliverables.
- is usually defined at the work package level.
Work Packages or Tasks are:
- activities that can be broken down into tasks by the work package owner.
- is an element of project work that requires action to produce a deliverable.
- shares some common characteristics such as expected duration, budget and resources.
Thursday, December 13, 2007
PMP Application Checklist
Prior to submitting your application, please make sure that you have checked all of the following:
Category I
- I have written my name as it appears on the identification that I will present when I take the PMIC examination
- I have included a current resume
- I have included proof of my degree
- I have included payment information
- My Experience Verification Form(s) dates back at least 3 years from the date of application
- My Experience Verification Form(s) does not date back farther than 6 years from the date of application
- My Experience Verification Form(s) reflects a total of at least 4500 hours
- When I count the months listed on my Experience Verification Form(s), the total is at least 36 (not counting gaps or overlap)
src="http://pagead2.googlesyndication.com/pagead/show_ads.js">
Category II
- I have written my name as it appears on the identification that I will present when I take the PMIC examination
- I have included a current resume
- I have included payment information
- My Experience Verification Form(s) dates back at least 5 years from the date of application
- My Experience Verification Form(s) does not date back farther than 8 years from the date of application
- My Experience Verification Form(s) reflects a total of at least 7500 hours
- When I count the months listed on my Experience Verification Form(s), the total is at least 60 (not counting gaps or overlap)
* The above information is obtained from the PMP Resource mailing list.
Saturday, December 8, 2007
Project Time Management in PMP
- Activity Definition
Identify the specific scheduled activities that need to be performed to produce the various project deliverables. - Activity Sequencing
Identify and document the dependencies among the scheduled activities. - Activity Resources Estimation
Estimate the type and quantify of resources that will be needed to complete each scheduled activity. - Activity Duration Estimation
Estimate the number of work periods that will be needed to complete each scheduled activity. - Schedule Development
Analyze activity sequence, duration, resource and schedule constraint to create the project plan. - Schedule Control
Control changes to the project schedule.
Friday, December 7, 2007
Scope Control in PMP
Scope Control is the process of holding changes to project scope in check by:
- ensure that changes are agreed upon.
- evaluate change requests to determine the actual need and impact of the change to the project objective.
- manage the actual change to ensure that they are implemented correctly and effectively.
Scope Verification with Inspection
- Scope verification is a process of formalizing acceptances of the completed project deliverables and project scope by stakeholder.
- Inspection is the tools and technique required for Scope Verification. It includes product reviews, audit, walkthru, etc. This ensure all work and deliverables meet the requirements and acceptance criteria.
Monday, December 3, 2007
Create WBS with Bottom Up Approach
- The lower-level components are necessary and sufficient for the completion of each decomposed item.
- Each element is described as a deliverable and is distinguishable from all other deliverables.
- Each element can adequately budgeted, scheduled and assigned to an individual or group.
Key Terms in WBS
- Code of Account / Control Accounts
- a system by which WBS elements are uniquely numbered.
- allows these individual WBS components to be more easily tracked, especially in the area of performance and costs. - Work Packages
- A deliverable or project work component at the lowest level of each branch of WBS.
- Divided further into scheduled activities. - WBS Dictionary
- Can be used as part of a work authorisation system to inform team members of when their work package is going to start, scheduled milestones and etc.
- It also contains a number identifier, control account, who is responsible for the work, schedule and milestones.
Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) in PMP
- A WBS is a logical grouping of project deliverables arranged in a hierarchical structure.
- A WBS defines the total scope of work required to complete the project.
- The deliverables and their component sub-deliverables are represented on the WBS in levels of descending order.
Thursday, November 29, 2007
Some Earned Value Formulas - From PMP Resource (for your PMP exam preparation)
The following are extracted from "PMP Resources":
The PMP exam is big on terminology. These are the basic Earned Value Terms you need to know. If you are studying to pass the PMP exam you should know these by heart and be able to derive them in case you are heartbroken. They really are fairly simple. In order from first to last:
BAC = Budget at Completion (Project budget)
AC = Actual Cost of the Work Performed
EV = Earned Value
EV = Budgeted Cost of the Work Performed
EV = % complete times BAC
PV = Planned Value
PV = Budgeted Cost of the Work Scheduled
CV = Cost Variance
CV = EV – AC
CPI = Cost Performance Index
CPI = EV/AC
SV = Schedule Variance
SV = EV – PV
SPI = Schedule Performance Index
SPI = EV/PV
EAC = Estimate at Completion
EAC = BAC/CPI
ETC = Estimate to Complete
ETC = EAC – AC
VAC = Variance at Completion
VAC = BAC – EAC
Note that the acronyms are slightly different from what was used a few years ago and is still widely used by old timers. PMI simplified the terms by dropping a letter here and there. The fundamentals are the same though.
You can also refer to http://groups.google.com/group/PMP-Preparation.
Sunday, November 25, 2007
Introducing Scope Definition in PMP
- What is Project Objective?
Project Objective is the criteria used to measure whether a project is successful or not. Specific in terms of scope, Quantitative Approaches, Realistic and attainable, Consistent / compliant with plans. - What is the difference between product and project scope?
Product scope is requirements that related to the product of the project.
Project scope is the work you need to do to deliver the product of the project. - What is the scope baseline?
Measurement of success on the project include whether the requirement have been met and whether the scope baseline has been met. It includes the project scope statement, WBS and WBS dictionary.
Scope Management Plan in PMP
- Identify a process that all deliverables will be accepted by the customer.
- Develop and maintain the project's WBS.
- Identify and control changes in project scope.
* Scope Creep refers to any uncontrolled change in a project.
Friday, November 16, 2007
Project Scope Management
- Create a Scope Management Plan
This includes documenting how the project scope should be defined, verified, controlled and how Work Breakdown Structure will be created and defined. - Create a Scope Statement
This includes developing a detailed project scope statement as the basis for future project decisions. - Create a Work Breakdown Structure (WBS)
This includes subdividing the major project deliverables and project work into smaller and more manageable components. - Scope Verification
This includes formalizing acceptance of the completed project deliverables. - Control a Project Scope
This includes controlling changes to the project scope.
Tuesday, November 13, 2007
Project Management Knowledge Areas Summary
I was reading the Project Management Knowledge Areas Summary by PMP Exam Resource and found that they have a very good summary on the Project Management Knowledge Area.
I have enclosed it below for your reference:
The PMBOK® Guide defines project management knowledge areas as:
- Project Integration Management,
the processes required to ensure that the various elements of the project are properly coordinated. It consists of project plan development, project plan execution, and overall change control. - Project Scope Management,
the processes required to ensure that the project includes all the work required, and only the work required, to complete the project successfully. It consists of initiation, scope planning, scope definition, scope verification, and scope change control. - Project Time Management,
the processes required to ensure timely completion of the project. It consists of activity definition, activity sequencing, activity duration estimating, schedule development, and schedule control. - Project Cost Management,
the processes required to ensure that the project is completed within the approved budget. It consists of resource planning, cost estimating, cost budgeting, and cost control. - Project Quality Management,
the processes required to ensure that the project will satisfy the needs for which it was undertaken. It consists of quality planning, quality assurance, and quality control. - Project Human Resource Management,
the processes required to make the most effective use of the people involved with the project. It consists of organizational planning, staff acquisition, and team development. - Project Communications Management,
the processes required to ensure timely and appropriate generation, collection, dissemination, storage, and ultimate disposition of project information. It consists of communications planning, information distribution, performance reporting, and administrative closure. - Project Risk Management,
the processes concerned with identifying, analyzing, and responding to project risk. It consists of risk identification, risk quantification, risk response development, and risk response control. - Project Procurement Management,
the processes required to acquire goods and services from outside the performing organization. It consists of procurement planning, solicitation planning, solicitation, source selection, contract administration, and contract close-out. - Professional Responsibility,
the tasks, knowledge, and skills required to ensure integrity, contribute to knowledge base, apply professional knowledge, balance stakeholder interest, and respect differences.
Friday, November 2, 2007
PMI Project Management 2007 Salary Survey
- Based on self-reported salary information from more than 5,500 project management practitioners.
- Based on compensation data in the 19 countries surveyed.
- 95% of the respondents total compensation increased over the past 12 months. Out of which 40% have at least 5% increase.
- 98% of the respondents expected the total compensation to increase in the next 12 months. Out of which 43% expecting an increase of at least 5%.
(For more information, please refer to the Oct issue of PMI today.)
Thursday, November 1, 2007
How to Select a Project?
It should meet:
- A market demand
- An organisation need
- A customer request
- A technological advance
- A legal requirement
Project Portfolio Management
What is Project Portfolio Management:
- A collection of projects
- A line of business
- Based on strategies within an organisation
- A guidance of senior management
Saturday, October 27, 2007
Project Selection Method Key Terms - Opportunity and Sunk Cost
- The opportunity given up by selecting one project over another.
Sunk Cost is:
- Non-recoverable project spent on the existing or last project. This is not related to bad debt as bad debt is over budget).
Project Selection Methods Key Terms - Depreciation
- Straight Line Depreciation
The same amount of depreciation is taken each year. - Accelerate Depreciation
Depreciates faster than straight-line (eg Double declining Balance).
Project Selection Methods Key Terms - Benefit Cost Ratio
- if the value is > 1, it means the benefits are greater than the cost.
- if the value is < style="font-weight: bold;">costs are greater than the benefits.
- if the value is = 1, it means the costs and benefits are the same.
Project Selection Methods Key Terms - Payback Period
- The time period it takes to recover your investment in the project before the company starts to accumulate profit.
Friday, October 26, 2007
Present & Net Present Value
Present Value is:
- future value of the money in the today's terms.
- Formula: PV = FV / (1+r)n
(where PV = Present Value, FV = Future Value, r = interest rate, n = number of period)
Net Present Value is:
- the present value of the otal benefits (income or revenue)
- allowed for a comparison of many projects and to select the best to initiate
Sunday, October 21, 2007
Project Measurement
- Scoring models
- Peer review
- Economic models
Mathematical models (Constrained Optimisation) that use:
- Linear programming
- Dynamic programming
- Integer programming
- multi-objective programming
Project Selection Method
- Feasibility analysis may be conducted using a formal study or an informal brainstorming session. It may also be used to compare alternative solutions to select the one that is the best fit for the organization.
- Cost-Benefit analysis compares the predicted costs and benefits of a project.
Configuration Management System
The following areas should be integrated into Change Control System:
- Scope
- Cost
- Schedule
- Contract
- Risk
- Manage Team
- Manage Stakeholder
- Quality
Friday, October 19, 2007
New Version of PMP Credentials Handbook
http://www.pmi.org/PDF/PDC_ PMPHandbook.pdf
Friday, October 12, 2007
Common Project Estimation Techniques
Analogous Estimation (Top-down)
- Pros
Can ensure no work is inadvertently omitted from work estimate - Cons
Can sometimes be difficult for lower-level managers to apportion cost estimates.
Bottom-up Estimation
- Pros
Is very accurate and gives lower-level managers more responsibility. - Cons
May be very time consuming and can only be used after the work breakdown structure (WBS) has been well defined.
Parametric Estimation
- Pros
Using parametric model is not time consuming. - Cons
May be inaccurate depending on the integrity of the historical information used.
Responsibilities of Project Management Office (PMO)
- Manage the interdependence between projects
- Help provide resources including software, tools, templates, policies, etc
- Help gather lessons learned and make them available to other projects
- Terminate projects
- Involves more heavily during project initiation than later in the project.
Wednesday, October 10, 2007
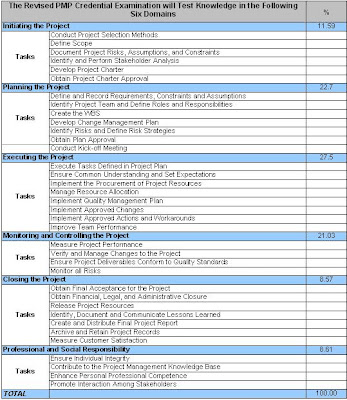
Revised PMP Credential Examination Test Knowledge Areas - for PMP Exam Preparation
Saturday, October 6, 2007
Who recognizes the PMP certification?
Some of the major companies that support project management certification include AT&T, Bell South, Bell Core, Bell Atlantic, US West, Motorola, GSK, Novartis, Citibank, HSBC, IBM, EDS, HP, ABB, Pacer International, Barclays, Microsoft, BBC, NCR, Eurotel, Shell, BP, and many others. Government agencies supporting PMP certification include the U.S. Defense Systems Management College, the U.S. Department of Energy, and Canada’s Department of National Defense.
PMP Examination Preparation Tips
http://groups.google.com/group/PMP-Preparation
Tips on taking the PMP exam
The PMP certification examination is a computer-based exam that is offered at PMI locations in the United States, Canada, and in other countries worldwide.The exam is based on information from the entire project management body of knowledge. The “Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge” (PMBOK), which is published by PMI, provides an outline of the topics covered.
Because the exam is computer based, participants can find out how they scored by reading the detailed report on performance that is available when the exam is completed.
Questions on the PMP exam are grouped by project management processes.The basic PMP exam is not industry specific. The PMI Certificate of Added Qualification (CAQ), which tests your knowledge of a particular industry, can be added to certify your expertise in Information Technology Project Management, Establishing a Project Management Office, and Project Management in the Automotive Industry.Tips for taking the PMP examPassing the PMP exam requires extensive preparation. Use the following tips and techniques as part of that preparation, which should also include developing a comprehensive understanding of the PMBOK concepts and terminology, practicing previous exam questions when possible, and attending a few project management-training courses.
Question-oriented tips
- There are certain questions that contain extra information. This information is irrelevant and it does not relate to the correct answer. Beware of such questions and remember it isn't necessary to use all the information provided to answer the question.
- Each question has only one correct answer. You need to select the most appropriate answer. Beware of choices that represent true statements but are not relevant. Be sure to read all the options before you select any one.
- You need to answer the questions from a PMI perspective—not from your own perspective, which you acquired through experience. Remember that PMI is trying to present an ideal environment for project managers that might be different from your own experience.
- Beware of answer choices that represent generalizations, which may be characterized by words such as always, never, must, or completely; these are often the incorrect choices.
- Look out for choices that represent special cases. These choices tend to be correct and are characterized by words such as often, sometimes, may, generally, and perhaps.
- The correct answer may not be grammatically correct.
PMI concept-oriented tips
- The project manager takes an active approach to the job by not waiting until a risk materializes and becomes a problem. This is an extremely important concept that might affect many questions on an exam. The project manager does not escalate problems to upper management or to the customer before fully analyzing them and identifying options. When answering a question related to what the project manager should do in a specific situation, you should rephrase the question to: What is the first thing the project manager will do given such a situation and given his or her proactive nature?
- Assume that lessons learned and historical databases are available. This might not be true in a real life situation.
- PMI does not approve adding extra functionality without benefits or gold plating.
- Project managers have all kinds of soft and hard skills.
- The Work Breakdown Structures (WBSs) are wonderful tools.
- Roles and responsibilities need to be properly defined.
General tips
- You should memorize all formulas, especially the Earned Value and PERT.
- Practice eliminating the completely implausible options first.
- There is no penalty for guessing; thus, do not leave any question blank.
- There will always be those situations where you have no idea what the question is asking.
- Use educated guessing to select the most appropriate option. Remember, you have only 80 seconds for each question. If you do not know the answer of a question, mark it and move on and revisit it later if you have time.
- Answer the questions based on the PMBOK concepts first, then consider your experience. If they are in conflict, the PMBOK wins.
Thursday, October 4, 2007
Project Management Process
- Initiating Process
Involve defining the need for the project and obtain a commitment to proceed. - Planning Process
Use to develop a strategy for how to accomplish the work in a project. - Executing Process
Involve carry out the strategy for the project. - Controlling or Monitoring the Process
Check and measure the required progress in the project. This also includes any corrective actions needed to get back on track. - Closing Process
Involve handing off the project, gain formal acceptance and perform administrative and contractual closure.
Project Management Balance Contraints
- Customer satisfaction
- Cost
- Time
- Risk
- Scope
- Quality
These constraints are set by priority and impact of changes involved directly or indirectly.
Furthermore, it is to note that a change to anyone of the constraints, the overall project should be evaluated to ensure that other constraints are not affected.
Monday, October 1, 2007
Organizational Structure Pop Quiz for PMP Exam
A. Functional Manager
B. Team Member
C. Project Manager
D. Technical Manager
2. Project team member are most likely to work full-time on a project in which of the following organizational structures?
A. Functional
B. Weak Matrix
C. Strong Matrix
D. Projectized
3. Tim is the project manager of the XXX project. His organization is a classic functional environment. His level of authority as a project manager can be best described as:
A. Low
B. Moderate
C. Balanced
D. High
4. Complex projects involving cross-disciplinary efforts are most effective managed by:
A. Multiple lead project manager
B. A function organization
C. A strong matrix organization
D. A strong traditional manager
(To see the answers, highlight this whole topic by right click on the mouse and drag down. If you are not able to do this, please leave me a comment.)
Answers:
1. A
2. D
3. A
4. C
Friday, September 28, 2007
Organizational Structures in PMP
Functional
Functional organizations are entities that have a clear division regarding business units and their associated responsibility. Project managers in functional organizations have the following attributes:
- Little power
- Little autonomy
- Report directly to a functional manager
- The project manager may be known as a Project Coordinator or Team Leader
- The project manager's role is part-time
- The project team is part-time
- The project manager may have little or no administrative staff to expedite the project management activities
Matrix Structure
Matrix structures are organizations that have a blend of departmental duties and employees together on a common project. The project team member to be from multiple departments working toward the project completion. Team member will report to multiple project managers and functional managers.
Weak Matrix
In a weak matrix structure, the project team may come from different departments but the project manager reports directly to the functional manager. The project manager has the following attributes:
- Limited authority
- Management of a part-time project team
- Project role is part-time
- May be known as a project coordinator or team leader
- May have part-time administrative staff to help expedite the project
Balance Matrix
In a balance matrix, the project manager has more time and power regarding the project than a weak matrix. The attributes of a project manager in this structure are:
- Reasonable authority
- Management of a part-time project team
- Full-time role as a Project Manager
- May have part-time administrative staff to help expedite the project
Strong Matrix
Strong matrix equates to a strong project manager. The project manager has the power and time required for the project. The attributes are:
- A reasonable to high level of power
- Management of a part-time to nearly full time project team
- Full-time role as a Project Manager
- Has a full-time administrative staff to help expedite the project
Projectized Structure
The project manager in a projectized structure may have complete power over the project team. Project manager in a projectized structure enjoy a high level of autonomy over their projects but also have a higher level of responsibility regarding the project success. The attributes are:
- High to complete authority over the project
- Work full-time on the project with his team
- Has a full-time administrative staff to help expedite the project
Composite Organizations
A composite organization is a blend of multiple organization types as listed above.
Thursday, September 27, 2007
PM Work Objective and Approach
- Knowledge
- Skills
- Tools
- Techniques
to the project activities to meet project requirements.
As for the work approach, it includes:
- SMART (Specific, Measureable, Archievable, Realistic and Time Bound)
- Identify Requirements
- Establish Clear and Achievable Objectives
- Balance Contraints
- Adapt specifications and plans to address the different concerns of the stakholders
Tuesday, September 25, 2007
Tips for passing the PMP certification exam
http://articles.techrepublic.com.com/5100-10878-5034989.html
Monday, September 24, 2007
PMP Pop Quiz 1
Stakeholders have ability to influence the final outcome of the project:
A. Later in the project life cycle
B. Earlier in the project life cycle
C. Anytime during the project life cycle
D. earlier in the project life cycle but increase over the life of the cycle
Q2
All of the following are part of the team's stakeholder management effort except?
A. Giving stateholder extra
B. Indentify stakeholder
C. Determining stakeholders needs
D. Managing stakeholders expectation
(To see the answers, highlight this whole topic by right click on the mouse and drag down. If you are not able to do this, please leave me a comment.)
ANS:
Q1 - C (Stakeholder has influence throughout the project life cycle)
Q2 - A (In PMP, you should give the stakeholder no more no less)
Saturday, September 22, 2007
How to Manage Stakeholder in Project Lifecycle?
- Identify stakeholders in all phases of the project.
- Access their knowledge and skills to have a common background.
- Analyze and keep them involved (work as a team).
- Get their signoff and formal acceptance during closure.
Monday, September 17, 2007
What is a Stakeholder?
- Sponsor
- Customer
- PM
- Team
- End User
- Society / Citizens
- Internal / External
What should the PM deal with Stakeholder?
- Identify them
- Determine all their requirements
- Determine their expectations
- Communicate with them
- Manage their influence
What is a Project?
- Temporary
- Unique
- Done for purpose
- Interrelated activities
- Progressively elaborated
Friday, September 14, 2007
PMP Exam Prep, Fifth Edition: Rita's Course in a Book for Passing the PMP Exam

I have been reading a number of books on PMP exam preparation and I have also done some research on the best book available. In conclusion, this guide from Rita Mulcahy is of the highest quality.
I have extracted the editorial review from Amazon and it is listed below:
Rita's book is boon to men and women preparing to take PMI's certification examination. --- J. Davidson Frame, Ph.D., PMP and Past PMI Director of Certification
Vijay K. Verma, author of Organizing Projects for Success
"This comprehensive resource is a "must read" for those aspiring to be certified as a PMP..." --This text refers to an out of print or unavailable edition of this title.
Product Description
Can you imagine valuing a book so much that you send the author a "Thank You" letter?
Tens of thousands of people understand why PMP Exam Prep by Rita Mulcahy, PMP, is a worldwide best-seller. Is it Rita's years of PMP exam preparation experience? The endless hours of ongoing research? The interviews with project managers who failed the exam, to identify gaps in their knowledge? Or is it the razor-sharp focus on making sure project managers don't waste a single minute of their time studying any more than they absolutely have to? Actually, it's all of the above.
PMP Exam Prep, Fifth Edition by Rita Mulcahy contains hundreds of updates and improvements from previous editions--including new exercises and sample questions never before in print. Offering hundreds of sample questions, critical time-saving tips plus games and activities available nowhere else, this book will help you pass the PMP exam on your FIRST try.
From the Publisher
This is the 4th edition of the PMP Exam Prep, often called "Rita's book" by project management students, which has easily become the standard training material to help project managers pass the PMP exam. PMP Exam Prep is being used in over 43 countries.
It is more than a series of sample exams. It is a comprehensive guide to get ready to pass the PMP exam.
PMP Exam Prep goes beyond the material contained in the PMBOK incorporating input about project management from around the world. The emphasis on this publication is the tools you need to pass the exam and apply project management principles to real-world situations.
Since the world of project management is constantly being updated, RMC prides itself on keeping its materials as up-to-date as possible with frequent edits and printings. --This text refers to an out of print or unavailable edition of this title.
From the Author
"I have tried to make the PMP Exam Prep a truly comprehensive guide to passing the PMP exam. I wanted it to be more than a rehash of the PMBOK or a series of exam questions, but a study guide that uses accelerated learning techniques to give you the most information in the least amount of time."
"I also wanted to use my experience training students to pass the PMP exam to help PMP hopefuls understand what to study and how to study and give them the best chance of passing." --This text refers to an out of print or unavailable edition of this title.
About the Author
Rita Mulcahy, PMP, has helped tens of thousands of project managers pass the PMP exam. She is an internationally-recognized expert on project management techniques, advanced project management theory, risk management and the PMP exam. Rita has over 14 years and US $2.5 billion worth of hands-on project experience, as well as 5 best-selling project management resources to her credit. She speaks to thousands of executives and project managers each year, and has a reputation for helping people to learn and to have fun while doing it.
Thursday, September 13, 2007
PMP Exam Information
For PMP Examination, the following are the details:
- Exam Version : Sep 2004 ( PMBOK Third Edition )
- No of Questions : 200 ( 25 Questions non-countable )
- Exam Duration : 4 Hours
- Required Passing Score : 53%
- Exam Fee : US$ 555.00 ( Non-PMI® Member ) / US$ 405.00 ( PMI® Member )
- PMI® Membership Fee : US$109.00 + US$10.00 ( Application Fee ) - So it is cheaper if you join PMI before taking the exam.
- Exam Period : Any avaliable time of Exam Center.
- Exam Procedure :
- Candidate submit their PMP Exam Application online ( Instructor will advice how to do so on the first lesson )
- Wait for PMI® approves your application and issue Eligibility ID, normally within 7 working days
- Register PMP® exam via www.2test.com by using the your Eligibility ID
- Check for Exam Center available time and Schedule the Exam
- Take your exam
Wednesday, September 12, 2007
What is covered in PMP Certification
In PMP, the following topics are covered. To pass the exam, you do not need to know the details of each process. However, you should know what is the input and output of each process and how they integrate together.
- Initiate project
- Plan project work and work breakdown structure
- Develop project schedules, cost estimates, and budgets
- Plan project quality, staffing, and communications
- Analyze project risk
- Plan project procurement
- Execute project work
- Monitor and control project work
- Monitor and control project schedule and costs
- Monitor and control project quality, staffing, and communications
- Monitor and control project risks and contracts
- Close project
What is PMP

The Project Management Professional (PMP®) Credential
Individuals who hold PMI’s PMP credential demonstrate a proficient level of project management leadership skills, and as a result are able to command salaries that exceed those of their non-credentialed counterparts.
To be eligible for a PMP credential, you must meet specific guidelines that objectively measure experience, education and professional knowledge. You also must agree to adhere to the  PMI Code of Ethics and Professional Conduct and pass a rigorous multiple-choice examination that assesses your abilities in project management.
PMI Code of Ethics and Professional Conduct and pass a rigorous multiple-choice examination that assesses your abilities in project management.
Eligibility
- • Applicants must have 35 hours of specific project management education.
- • With a Bachelor’s Degree (or the global equivalent): Applicants must have a minimum three years’ professional project management experience, during which 4,500 hours are spent leading and directing project tasks, up to eight years from the time of application.
- • Without a Bachelor’s Degree (or the global equivalent): Applicants must have a minimum five years’ professional project management experience, during which at least 7,500 hours are spent leading and directing project tasks, up to eight years from the time of application.
The PMP Credential Examination
This four-hour examination composed of 200 multiple-choice questions measures your ability to apply knowledge, skills and techniques used in project management. The examination is developed by groups of individuals from around the globe who hold the PMP credential and is routinely reviewed and revised to ensure the best and consistently objective assessment.
(obtained directly from PMI's website: http://www.pmi.org/CareerDevelopment/Pages/Obtaining-Credential.aspx)
Suggested Study Materials
- PMP-Preparation Recommended Books
- PMP Exam Prep, Fifth Edition: Rita's Course in a Book for Passing the PMP Exam
- A Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge, Third Edition (PMBOK Guides)
- The PMP Exam: How to Pass On Your First Try (Test Prep series)